22 Oct 2018
Abstract
The maintenance of autoreactive B cells in a quiescent state is crucial for preventing autoimmunity. Here, we identify a variant of human IgG1 (hIgG1-G396R), which positively correlates with systemic lupus erythematosus. In induced lupus models, murine homolog G390R knock-in mice generate excessive numbers of plasma cells, leading to a burst of broad-spectrum autoantibodies. This enhanced production of antibodies is also observed in hapten-immunized G390R mice, as well as in influenza-vaccinated human G396R homozygous carriers. This variant potentiates the phosphorylation of IgG1 immunoglobulin tail tyrosine (ITT) motif. This, in turn, alters the availability of phospho-ITT to trigger longer Grb2 dwell times in immunological synapses, leading to hyper-Grb2-Btk signaling upon antigen binding. Thus, the hIgG1-G396R variant is important for both lupus pathogenesis and antibody responses after vaccination.
[Image]
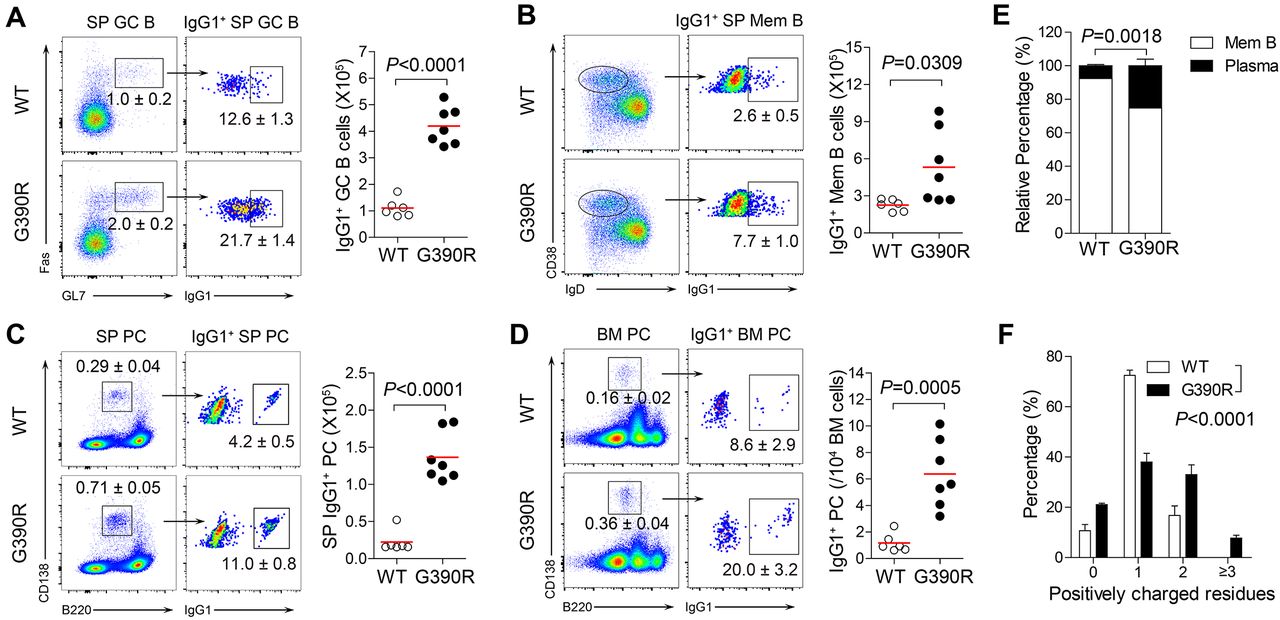
The IgG1-G390R variant promotes plasma-cell accumulation in induced autoimmune models.
(A to D) Flow cytometric analyses of IgG1+ GC B cells, memory B (Mem B) cells, spleen (SP) and bone marrow (BM) plasma cells (PC) in WT (n = 6) and G390R (n = 7) mice at week 6 after bm12 splenocyte induction. GC B cells (GL7+, Fas+) were pre-gated on B220+ cells. Percentage (means ± SEM) of B cell subsets and corresponding comparison of cell numbers (right) are indicated.
(E) The relative percentage (means ± SEM) of IgG1+ plasma cells and memory B cells in fate-selected cells of WT in comparison to G390R mice.
(F) Frequency (means ± SEM) of Igγ1 CDR3 with different numbers of positively charged amino acids in IgG1+ bone marrow plasma cells (WT CDR3, n =64; G390R CDR3, n = 66) from bm12-induced WT (n = 3) and G390R mice (n = 3). Unpaired two-tailed t-tests, (A) to (E). Two-way ANOVA, (F). Bars denote means. Representative data are from at least two independent experiments in (A) to (F).
